Today, most household plots have ceased to be used primarily as a place for planting fruit trees or garden crops. Increasingly, you can find ennobled gardens, where the main role is played by landscape design. There are many plants whose appearance can decorate any place. And the most popular among them are decorative pine trees - conifers, which have unpretentiousness in care and preserve beauty even in the cold season. Their bright representative is the Jacobsen pine.
Description and characteristic of Jacobsen pine
According to the description, a variety of mountain pine Jacobsen (Pinus mugo Jakobsen) was bred in Denmark at the end of the 90s of the last century. It is an evergreen dwarf bush with all the characteristics of a bonsai. The curved branches of the plant are covered with dark green, densely growing needles, forming light brown “pompons” at the ends. The branches themselves are quite thick and strong, have a horizontal direction of growth, and in winter (in February), covered with white buds.
Did you know? The oldest tree on the planet is Methuselah pine. According to scientists, her age is about 5 thousand years.
Over time, their bases are exposed, thereby acquiring the very same forms of bonsai that are so appreciated by lovers of decorative conifers. The shrub is characterized by slow growth - in one year it adds no more than 4 cm. Thus, at the age of 10 years, its height reaches 0.5 m, and the crown diameter is not more than 0.9 m. Most often, Jacobsen pines can be found in compositions of alpine hills or heather gardens. Such shrubs look great both in single and in group plantings.
Landing Features
The procedure for planting Pinus Jakobsen mountain pine seedlings is not difficult. The main thing that you should pay attention to is the right choice of young bushes and the place of further growth. The appearance of the shrub in the future, as well as its development, will depend on these parameters.
Video: planting a mountain pine
Terms and conditions
Pine of this variety belongs to photophilous plants, and therefore, when choosing a place, it is necessary to stay in well-lit (partial shade allowed) and open areas. Deficiency of sunlight can lead to elongation of shoots and faded needles. The shrub perfectly takes root on any kind of garden soil, even with a poor structure or high acidity.
However, the best results can be achieved in the soil, which is as close as possible to their natural habitat - sand or sandy loam (acid reaction is weak). With a high sand content, clay is additionally added to the soil. The optimal planting time is considered to be spring (mid-April - early May) or early autumn (early September).
Preparatory work
Immediately before planting, both the chosen place and the seedlings themselves must undergo the preparation procedure. To do this, the soil in which the bush will grow is cleaned of perennial weeds, after which the landing pit itself is prepared. At the same time, the top layer of the earth (fertile) is thrown to the side (then it will be mixed together with fertilizers). Saplings aged 3-5 years are optimal for planting, since their root system is sufficiently developed and easily adapts to a new place. When buying a seedling in a pot, it is recommended to choose only local nurseries. This is because the plant will be much easier to take root in the familiar climate. The root system of a young bush immediately before planting is well moistened - this will protect it from injuries when placed in a landing pit.
Saplings aged 3-5 years are optimal for planting, since their root system is sufficiently developed and easily adapts to a new place. When buying a seedling in a pot, it is recommended to choose only local nurseries. This is because the plant will be much easier to take root in the familiar climate. The root system of a young bush immediately before planting is well moistened - this will protect it from injuries when placed in a landing pit.
Important! The fabric or net that protects the rhizome is not removed when planting. In the soil, it will quickly decay and will not interfere with plant growth.
Step-by-step landing instructions
The landing process consists of several stages:
- The landing pit is prepared in advance (at least 2-3 weeks before the intended landing) - this allows the soil to settle and evenly moisten.
- The size of the hole directly depends on the size of the root system of the seedling (the roots should not be bent), as well as the soil of its future growth (heavy and clay soil requires large pit sizes). But, on average, it is from 7 to 10 cm wide and up to 1 m deep.
- The bottom of the hole is laid with drainage, which can be broken brick, crushed stone or expanded clay, followed by a layer of coarse sand or gravel. The thickness of the drainage layer is 20 cm.
- The top layer, which was obtained in the process of digging a hole, is mixed with sheet soil in equal proportions, and a fifth of sand is also added. Additional introduction of compost, rotted manure or complex nitrogen fertilizer (about 50 g) will not be out of place.
- The soil mixture is poured into the planting pit and a sapling is put on the formed mound. At the same time, the root neck should be at ground level.
- The ground is carefully tamped with a foot, and a trunk circle is formed around the seedling. The soil is abundantly watered and mulched. As mulch, you can use pine needles or peat.

Further care
Further care is not particularly difficult. At first, while the seedlings take root in a new place, they are protected from direct sunlight. This can be done with the help of spruce branches or spunbond. In addition to the main irrigation, in the conditions of hot summer, young bushes are additionally sprayed with water from above. But you should know that a similar procedure can only be carried out in the evening, in order to avoid sunburn on the plant.
Important! They fertilize the mountain pine exclusively in the spring, since the application of top dressing in the fall can interfere with the lignification of young shoots and, as a result, cause them to freeze.
Otherwise, agricultural activities are carried out as standard and consist of:
- glaze - in the first month of life, moisture is applied to the soil weekly, using 10–20 l of water for each bush, and in the future, as necessary, and only in the summer period;
- loosening the soil - in the case of strong compaction of the soil and after irrigation (in this case, the proximity of the roots to the surface of the earth should be taken into account);
- top dressing - are introduced in the first 2 years of the plant’s life, in the spring, and consist of complex mineral fertilizers, at the rate of 30 g per shrub.
Also, the first time (2-3 years) young bushes are covered for the winter, and the trunk circle is mulched with peat. This not only protects them from frost, but also helps to avoid sunburn in early spring, as well as breaking the crown under the weight of snow. To do this, the branches are loosely fixed with soft twine, and on top they put on special covers for conifers. Do not forget about pruning. Due to the fact that the mountain pine initially has a good shape, the desired appearance is achieved by pinching young shoots 1/3 of the entire length. This provokes a thickening of the crown and a slowdown in plant growth. It is also recommended to remove broken and frost-beaten branches in spring.
Do not forget about pruning. Due to the fact that the mountain pine initially has a good shape, the desired appearance is achieved by pinching young shoots 1/3 of the entire length. This provokes a thickening of the crown and a slowdown in plant growth. It is also recommended to remove broken and frost-beaten branches in spring.
Pine diseases and control
Mountain pine, like other plants, can be susceptible to various diseases. Among the most common, note:
- Rust - a fungal disease characterized by the formation of yellow vesicular spots on the surface of the needles of a shrub. The peak of development occurs in the spring. Lack of timely treatment can cause a rapid spread of the disease and, as a result, drying and falling of needles, as well as a loss of decorative properties. To combat rust, the affected areas are removed from the bush and burned, and micronutrient fertilizers and immunostimulants are used on the plant itself. As a prophylaxis of the disease, it is highly not recommended to plant pine next to poplars or aspen, as well as black currants. All of these plants can become carriers of rust.

- Brown snow mold (brown shute) - a fungus that infects needles in the autumn, and the first manifestation can be seen in the spring. It has the appearance of a black-gray cobwebbed raid, which leads to the death of branches. The development of the disease contributes to prolonged high humidity and thickening of the bush. To get rid of mold, fungicidal treatment is used.
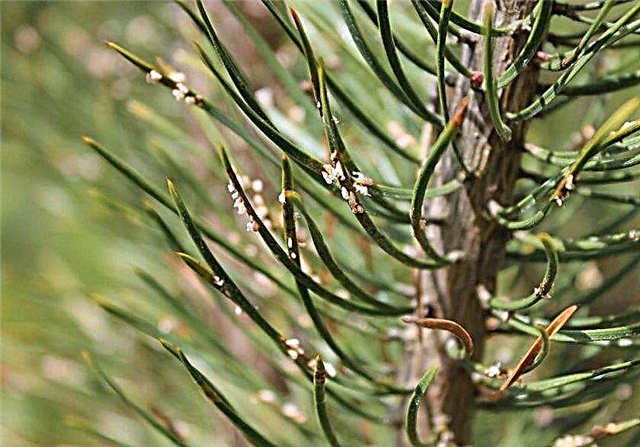

- Pine shoot cancer (white cancer or scleroderriosis) - fungal disease, which manifests itself in the form of redness at the junction of the needle with a branch. In the process of further development, the needles are completely painted in brown color and fall off at the slightest touch. At the same time, necrotic spots form on the shoots. As a treatment, infected bushes are treated with systemic fungicides at intervals of 20 days (from May to September).
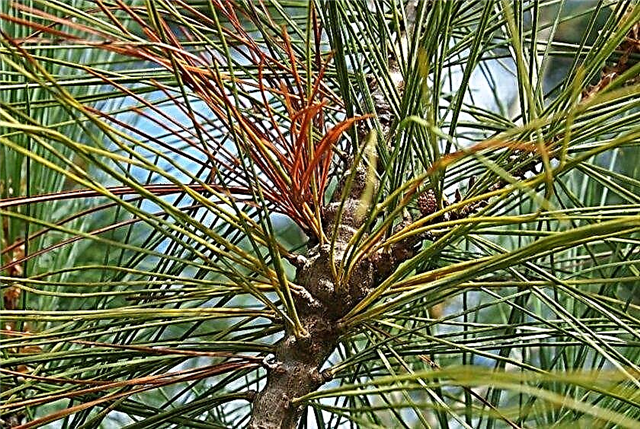

- Necrosis of the cortex - rotten disease, which is characterized by the death of tissues around the entire circumference of the shoots. At the sites of damage, rot is formed. To combat the disease, all infected areas are removed, and the pine itself is treated with a 1% solution of Bordeaux fluid. The same drug is used as a prophylactic in case of a long period of high humidity or lack of sunlight.

Like all pines, the Jacobsen variety can be attacked by pests.
Did you know? Word «Pine» sounds in Latin as "pinus", which means translated «rock». This plant got its name for its ability to cling to its roots and survive even on bare rocks.
Among them, the most dangerous are:
- Silkworm pine - is a caterpillar (length can reach 10 cm), which feeds on the needles of conifers. This insect perfectly tolerates cold, and with a large number, it can destroy entire bushes. As a pest control, insecticidal treatment is used.

- Scoop - a pest that feeds on both needles and its kidneys. Despite a fairly short period of activity (30–35 days), this caterpillar can cause serious damage to the young bush and cause it to dry out. Insecticides are used to get rid of the insect.

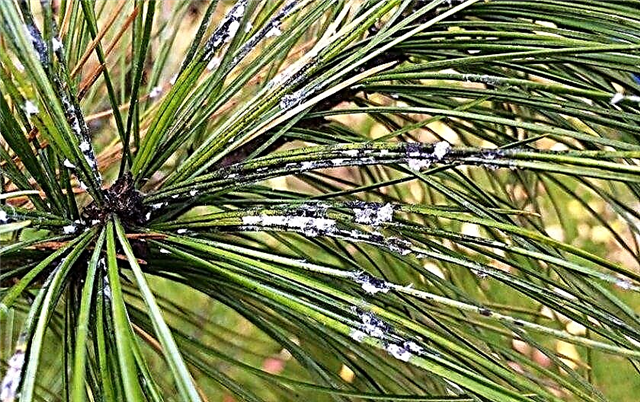
- Hermes - Aphids, which, eating, sucks juices from needles. To learn about the attack of these pests is simple - by the formed white coating on the branches. Upon closer examination, it becomes apparent that it is a colony of aphid larvae. In the fight against them, insecticidal drugs are used, the treatment of which is repeated every 4 weeks.

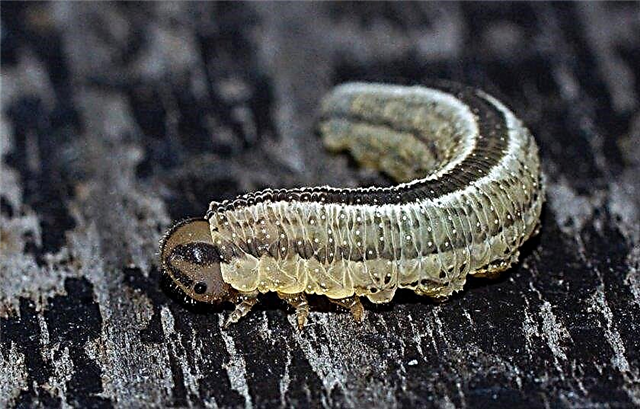
- Sawflies - Larvae of small sizes (about 8 mm in length) that live on the shoots of needles and feed on its needles. This leads to the formation of yellow spots on the crown and the drying of individual branches. During treatment, the root circle of the pine is dug up, and the plant itself is treated with insecticidal preparations.

Jacobsen pine can often be found in personal plots. She is valued not only for her beautiful appearance and organicity in various group compositions. This evergreen shrub, due to its unpretentiousness in care, is easy to grow, which makes it popular both among professional gardeners and beginners of this business.