Variety Laura is one of the most common varieties of potatoes. Its tubers are distinguished by high commercial qualities and versatility of use, but at the same time the plants are unpretentious in care and can be grown in various climatic conditions. This article presents a description of Laura potatoes, planting features and rules for caring for bushes.
History of the variety
Potato Laura was bred by breeders of the company Europlant Pflanzenzucht GmbH (Germany), who wanted to create a new variety that could surpass the known Scarlett variety in yield. As a result of the work, this variety was obtained, which is considered the best in productivity among all types of potatoes with red peel. Today it has gained immense popularity in Europe, Ukraine, Russia and Belarus, as well as in the Baltic states.
Did you know? Potato was the first vegetable to be grown in space. It happened in 1995 year aboard the shuttle Columbia.
Description and characteristic
Due to its relatively early ripening, the Laura variety can be grown in regions with different climate conditions, but during severe drought its yield is markedly reduced. Plants and tubers have a number of characteristic features by which they can be distinguished from other varieties of potatoes.
 Potatoes with a starch content of 14% to 25% are considered “highly starchy”, which means tasty
Potatoes with a starch content of 14% to 25% are considered “highly starchy”, which means tasty
Description of varieties Laura:
- The harvest ripening period is about 80 days from the moment of planting in open ground.
- Laura potato bushes are tall and erect, covered with a large number of dark green leaves with a wrinkled surface.
- Flowering is plentiful and falls in mid-June. In this case, white or light purple flowers appear on each bush.
- The tubers are oval in shape and large in size. The mass of each of them is 90-150 g, and the length is about 7 cm.
- Productivity is 330-510 kg / ha. From one plant you can collect from 15 to 20 potatoes with a total weight of about 2 kg.
- The thin and smooth peel of the fetus is painted dark pink, and its surface is even. It has small eyes that do not remain on the pulp after peeling the potatoes.
- The dense pulp of the potato is painted yellow, which does not disappear after heat treatment. It contains about 16.5% starch.
- Potatoes have a great taste and can be used in cooking to prepare a wide variety of dishes, because they do not boil during heat treatment.
- Plants show moderate resistance to common diseases and pests.
Did you know? Among all countries, China ranks first in potato production. About 88 million tons of these tubers.
Positive and negative sides of the variety
Variety Laura has many advantages that distinguish it from other varieties of potatoes. Therefore, in Europe, it is often grown not only on small land plots, but also on an industrial scale.
- The main advantages of this culture include:
- high productivity;
- excellent presentation of potatoes;
- good taste;
- universality of the use of tubers;
- average early ripening of the crop;
- good storage and transportability;
- good immunity to diseases and pests;
- unpretentiousness to climate conditions and leaving.
- The disadvantages of potatoes Laura gardeners include such qualities:
- thin peel does not protect the fruit from mechanical damage;
- plants need fertile soil for a plentiful harvest;
- plants do not respond well to treatment with the herbicide Metribuzin - it is used to destroy weeds when growing potatoes on a large scale.
Planting potatoes in the open ground
Even a novice gardener can grow Laura potatoes on his plot. Planting this culture is quite simple and does not require special skills, however, it is necessary to carry out preliminary preparation of the soil and planting material, as well as choose the most suitable time for planting seed tubers into the soil. Potatoes should be planted at medium temperatures, preferably in the middle - the end of May, when the soil temperature is high enough
Potatoes should be planted at medium temperatures, preferably in the middle - the end of May, when the soil temperature is high enough
Soil requirements
In order to achieve high yields, this potato variety is recommended to be grown only on loose and fertile soils. For this, chernozem is best suited, as well as peat and sod-podzolic soil of neutral acidity.
Important! At the time of planting, the minimum temperature of the soil at a depth of 10-12 cm should be at least +8 ... + 10 ° C.
The basic rules for preparing the soil for planting the Laura variety are listed below:
- in the fall, before the onset of frost, all plant debris is removed from the site and digging the ground to a depth of about 30 cm;
- during autumn digging of the soil, 1 kg of rotted manure, 35 g of superphosphate and 15 g of potassium sulfate are applied to 1 m² of area;
- in the spring, the site is again dug up to a depth of 10-15 cm, after the ground has thawed and will be amenable to processing;
- to increase the resistance of potatoes to diseases and pests, the soil is disinfected a month before the tubers are planted - for this, it is watered with an aqueous solution of Formalin (250 ml of the drug per 10 liters of water) or Fitosporin (6 ml of the substance per 10 liters of water), spending on 1 m² about 10 liters of the mixture.
 Good precursors for potatoes are cereals and legumes, cabbage, cucumbers, pumpkin, corn and onions, and bad ones are sunflower and tomatoes
Good precursors for potatoes are cereals and legumes, cabbage, cucumbers, pumpkin, corn and onions, and bad ones are sunflower and tomatoesDates for boarding
When choosing the time for planting Laura potatoes, you need to consider the climate conditions of a particular region. Planting material immersed in too cold ground can rot and not germinate, and late frosts in April can completely destroy plantings of this variety. therefore in the southern regions, the Laura cultivar is planted in the soil at the end of April, and in the northern regions from mid-May.
Did you know? Potato pulp is 80% water.
Preparing planting material
To improve germination and protect the Laura variety from diseases and pests in the future, it is recommended that seed tubers are pre-prepared for planting. The procedure is carried out in April - 3-4 weeks before the planned planting of potatoes on the site.
To do this, perform these simple steps:
- sort out the planting material, removing rotten and damaged fruits - for planting, it is recommended to choose identical in size specimens weighing about 90 g so that the shoots appear evenly;
- 2 weeks before planting, transfer seed potatoes to a well-lit place - this will stimulate the formation of sprouts;
- before laying in the soil, immerse the tubers for half an hour in a solution of copper-containing preparations - this will increase the resistance of the culture to diseases and pests;
- it is possible to carry out additional disinfection of seed tubers with insectofungicides (for example, Prestige) by preparing a solution of 100 ml of the preparation and 6 l of water - the resulting mixture will be enough to spray 1 kg of tubers in order to protect it from pests. This procedure is carried out only if the gardener does not plan to eat young potatoes;
- for additional protection against the Colorado potato beetle, each potato can be sprinkled with wood ash powder;
- treat the fruit with a solution of gibberellin - this will stimulate the active growth of the plant and accelerate the emergence of seedlings.
Video: potato processing before planting
Landing technology
After preliminary preparation of the soil and planting material has been completed, they proceed to embed seed tubers in the ground. Laura potatoes can be planted with a comb or smooth method. In the first case, tuber wells are located on the top of the ridge formed from the soil, and in the second, on the flat surface of loose soil. But, regardless of the chosen method of planting, you need to arrange the plants on the site in even rows.
Step by step instructions:
- Mark the rows on the site, placing them at a distance of 60–70 cm from each other.
- In each row, dig holes about 10 cm deep. The distance between adjacent recesses in the row should be 25-30 cm.
- At the bottom of each hole put a handful of wood ash or a pinch of humus.
- Place the seed in the hole, placing it so that the sprout is pointing up. Sprinkle a recess with a layer of soil about 5 cm thick.
- After embedding planting material, level the soil surface in the area with a rake. If the ground is too dry, you can water the beds with a little water.
Video: planting potatoes
Care Features
The Laura variety is unpretentious in care, but to increase its productivity it is recommended to use standard agrotechnical techniques. Even when planting plants on a site with fertile soil, they need to be additionally fertilized during the growth process so that the potatoes do not lack nutrients. In addition, it is important to properly care for the soil in the beds and regularly fight against diseases and pests.
Important! Watering potatoes is recommended in the early morning to prevent the rapid evaporation of water from the soil.
Fertilizer and Watering Frequency
The variety under consideration responds well to watering, and in conditions of prolonged drought, it is necessary to irrigate the beds additionally so that the land does not have time to dry out very much. With enough rain, potatoes can be watered as needed. Experienced gardeners advise to irrigate the beds about 3 times for the entire growth of the crop.
Basic rules for watering bushes:
- potatoes are irrigated for the first time 3 weeks after emergence;
- the beds are watered repeatedly before flowering begins - at this time the plants spend a lot of energy on the formation of buds and are especially in need of water;
- the last time the plants are watered immediately after the disappearance of the inflorescences, providing them with moisture for the successful ripening of tubers;
- for uniform soil moisture in the area, it is recommended to use a drip irrigation system;
- at the ripening stage, potatoes are not irrigated - the bush spends a lot of effort on this process and becomes more vulnerable to infections, and waterlogging of the soil contributes to the development of fungal diseases.
It is equally important to provide the potato with a sufficient amount of nutrients; at the same time, at different stages of growth, the plant needs different types of fertilizers. The main recommendations for feeding bushes:
- nitrogen fertilizers are applied during the growth of green mass - 0.5 l of a solution prepared from 10 l of water, 1 tbsp. l urea and 1 tbsp. bird droppings;
- in the budding phase, you need to nourish the bushes with potash and phosphorus fertilizers - for this you need to dilute in 10 liters of water 2 tbsp. wood ash and 1 tbsp. potassium sulfate and superphosphate, watering each plant with 500 ml of the prepared nutrient mixture;
- after flowering under each bush make 0.5 l of a mixture of 10 l of water, 2 tbsp. superphosphate and 1 cup mullein;
- before flowering, it is recommended to carry out foliar dressing by spraying potatoes with nutritious infusion - for its preparation you will need 10 l of water, 20 g of superphosphate, 2 g of nitrate and potassium chloride and about 0.1 g of copper sulfate.
Video: feeding potatoes
Weed cleaning
An important place in the care of Laura potatoes is the proper tillage on the beds. The formation of large tubers and the overall crop yield depend on this factor.
The basic rules for processing soil around potatoes of this variety:
- periodically remove weeds throughout the entire growing season of the plant - weed grass draws nutrients and moisture from the ground, attracts pests and obscures young potato sprouts;
- carry out loosening of soil around potatoes - this procedure is carried out in combination with weeding the beds and facilitates the access of water and air to the roots;
- to cover the surface of the soil on the beds with a layer of mulch from dry straw - this will help to avoid the need for frequent watering of bushes and will reduce the number of weeds, keeping the earth moist and loose;
- after the tops of the bush has grown to 20 cm, carry out the earthing up of potatoes - this procedure enriches the soil with oxygen and promotes the formation of new stolons, increasing the yield indicators of the variety;
- 20 days after the first hilling procedure, it must be repeated.
Pest and Disease Control
The variety in question has good immunity to common pests and infections, but with improper care, the resistance of plants decreases and they can become ill. In this case, you need to notice the problem in time and immediately begin treatment.
Important! The last processing of potatoes with chemical preparations against pests can be carried out no later than 30 days before harvesting.
Potato Laura can be threatened by such diseases and pests:
- Blight (potato rot). The disease is fungal in nature and can affect the beds after flowering. In this case, brown spots appear on the leaves of the potato, and their inner surface is covered with a characteristic white coating. In the future, the infection spreads to tubers - when they are cut into flesh, brown spots are visible. To save potatoes from this disease, spraying with a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid or with the Kuproksat drug will help.

- Blackleg. This disease has a bacterial nature, and its main sign is the appearance of black plaque on the bottom of the potato stem. At the same time, the tops of the plant quickly turn yellow and dry, the bush is easily pulled out of the soil, and the tubers are covered with wet mucus and rot. The infection is not treatable, and diseased specimens must be removed immediately from the site.

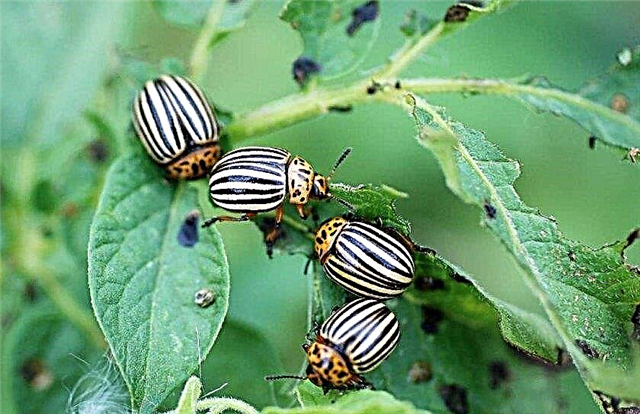
- Colorado beetle. Insects have a characteristic striped wing color and lay eggs on the plant, from which pink larvae appear. They eat up the green crown of potatoes, as a result of which the bush loses its leaves, tubers do not form, and the yield of the variety is noticeably reduced. With a small number of caterpillars and adult insects, they are collected manually, and with severe damage, use the Kinmix preparation according to the instructions.

- Wireworm. This pest lives on the surface of the soil and causes damage to potato tubers and the lower part of its stem, making through them through passages. Damaged tubers cannot be stored and rot, and the stalk begins to fade. You can cope with wireworms using traps of pieces of fresh potatoes and carrots planted on a wooden stick. They are buried in the ground to a depth of about 10 cm, and after a few days they are removed from the soil along with the accumulated pests.

- Bear This large insect lives underground and eats the roots and fruits of potatoes, making them unsuitable for storage. With a strong defeat of the roots, the bush begins to wither and dies. Signs of the appearance of the bear are round passages on the surface of the earth and nibbled potatoes. You can get rid of the insect with the help of hot pepper infusion (200 g of spice per 10 l of water) or special chemicals.

To prevent these difficulties, it is enough to perform the following actions:
- observe crop rotation;
- to select high-quality planting material for sowing;
- disinfect soil and seed tubers before planting;
- comply with the recommended layout of plants on the site;
- carry out proper soil care in the beds;
- carry out autumn digging of the soil.
Harvest recommendations
When planted in early May, the Laura potato crop ripens in August. In this case, you can wait until the tubers have reached technical maturity, or dig them out of the ground a little earlier. In the second case, they must be used immediately - at this stage, the peel is easily detached, which makes the potato unsuitable for storage.
Important! The main sign of tuber ripening is yellowing and wilting of the tops.
Basic rules for harvesting and storage of crops
- the bush is gently dug laterally with a fork, and then manually pick tubers from the ground, folding them in a bucket or basket;
- the harvested crop is laid out under a canopy on the street for drying - this process takes about 2 weeks;
- dried potatoes are sorted by size, removing damaged and rotten specimens;
- selected tubers are stored in a dark basement with good ventilation at an air temperature of +1 ... + 3 ° С;
- Stability of the variety, subject to all of the above conditions, is 90%, and the crop can be stored until the beginning of next summer.
 Variety Laura is considered to be one of the best varieties of potatoes, delighting farmers with its many positive qualities. Adhering to the recommendations for planting and care listed in this article, you can successfully grow this crop in your area, and the described rules for fertilizing and methods to combat difficulties will help increase the yield of the variety.
Variety Laura is considered to be one of the best varieties of potatoes, delighting farmers with its many positive qualities. Adhering to the recommendations for planting and care listed in this article, you can successfully grow this crop in your area, and the described rules for fertilizing and methods to combat difficulties will help increase the yield of the variety.