Among cabbage varieties, high-yielding Dutch hybrids deserve special attention. Ankoma F1 is one of those. This is a late-ripening hybrid of the first generation, intended for fresh consumption and further processing. Read about the features of the variety and the agricultural technique of growing this cabbage in a review.
Description of cabbage Ankoma
Ankoma F1 is a representative of medium-late varieties whose technical maturity occurs 120 days after emergence. Attractive round dense heads of cabbage weighing up to 4 kg are distinguished by high palatability.
The variety was introduced for registration in the State Register in 2002 and included in it in 2007. Originator - Rijk Zwaan Marne Aktiengesellschaft. Zoned for the Central regions of Russia.

Characteristics of cabbage Ankoma
Ankoma F1 (Ancoma RZ F1) is the company's leading product in the cabbage sector. It is characterized by marketable appearance, good storage and transportability. It tolerates adverse weather conditions, including drought, and shows a stable yield. Resistant to fusarium wilt and other fungal diseases.
The basic characteristics of the variety:
- leaf outlet: vertical or raised;
- head: round, dense, with thin leaves;
- leaves: medium-sized, roundish, slightly wavy along the edge, with a wax coating of medium intensity;
- outer stump: medium size;
- weight: 2.5-4 kg;
- texture: dense, crispy;
- tolerance: resistant to fusarium;
- ripening period: 120-130 days;
- palatability: high;
- productivity: 100–120 t / ha.
Did you know? In China, cabbage — symbol of wealth: both words are pronounced the same — "Tsai". Maybe this fact added the word “money” in the Russian language to the word “cabbage”.
The described cabbage can be grown on personal plots and on large farms, showing yields of up to 120 t / ha. It is recommended to plant it in seedlings, but it is also sown with seeds in open ground or in a greenhouse.
Productivity and fruiting
The yield of the variety, confirmed in the file of the State Register, is 418-610 kg / ha. The maximum yield obtained in the Smolensk region during variety testing is 714 c / ha. This indicator is affected by soil fertility and the number of sunny days during the growing season.
Application area
Early and medium grades, as well as all hybrids, are intended for use in fresh, stewed, boiled form: in salads, soups, main dishes, pies. Due to its nutritional properties and benefits, cabbage products are present almost all year round in our diet.
Learn about growing other varieties of cabbage:
Resistance to diseases and pests
Differences in resistance between varieties are observed in the field, both for foliage and for the root system. When testing varieties, only those diseases are distinguished whose resistance to which was shown in all fields. In the variety Ankoma F1, this is Fusarium wilt. The variety also shows moderate resistance to other fungal diseases.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- Grade advantages:
- high and constant yield;
- excellent taste;
- resistance to adverse weather conditions (including frost resistance);
- the ability to store until spring without loss of taste;
- excellent presentation of heads of cabbage, not deteriorating during transportation;
- resistance to fungal diseases;
- unpretentiousness in leaving.
Deficiencies of the variety are not identified. Features include the fact that in the Central regions of Russia it is desirable to grow medium-late cabbage in seedlings.

Growing rules
Cabbage is quite easy to grow: it is hardy, tolerates any weather conditions and is unpretentious in care. In order to get a good crop, it is advisable to choose the right site for cultivation with fertile soil and timely conduct basic agricultural activities.
Did you know? China is the largest producer of cabbage, and Russia — its largest consumer.
Planting seedlings
To apply the seedling method, you will need to prepare:
- seeds;
- priming;
- containers for growing.
Seeds before planting are disinfected in order to protect against pathogenic microflora. Accelerate biological processes in them using growth stimulants. Seedling containers are washed with soap or disinfected if used last season. The soil mixture is prepared independently or purchased in the store soil for vegetables.

The timing
Planting time depends on the climatic conditions of the region. At the time of transplanting seedlings into the soil, its age should be about 40 days. Therefore, if seedlings are planted in a permanent place at the end of May, then the seeds are planted on April 20–25. During the growing period, 3-5 real leaves should form on the plants.
Did you know? The folk sowing calendar advises to plant cabbage seedlings in the ground on May 18 — on the day of Irina the hotbed. And to finish harvesting this crop is recommended September 27th.
Soil preparation
Cabbage grows well in neutral or almost neutral soil. This vegetable should not be grown in acidic soils: this contributes to the infection of plants and soil with keel, a dangerous cruciferous disease. Be sure to check the acidity of the soil in which you are going to grow seedlings, and the land on the site.
In order to protect the future crop, the soil mixture is decontaminated. It is treated with boiling water or high temperature to destroy the eggs of pests. You can also treat it with a 3% solution of potassium permanganate to destroy pathogenic microflora.

Preparing planting material
Seed preparation consists of:
- calibration
- disinfection
- sprouting.
Calibration is the process of selecting germinating seeds. To do this, they are soaked for 5 minutes in 5% sodium chloride solution. Pop-up seeds are empty. They are thrown away, and the rest is washed from salt and disinfected with a 3% potassium permanganate solution.
Growth stimulator treatment is used to enhance plant immunity. This increases disease resistance and optimizes the development of cabbage. But such a procedure is not mandatory and is carried out at the request of the farmer.
Important! Nitrates that remain in the plant tissue after spraying with pesticides gradually pass into the stump, so it must be discarded. Only leaves are used for food.
Germination of seeds will accelerate the development of plants, in addition, you can control the percentage of germination of seeds, since only those that will germinate will be planted. To do this, they are laid on a saucer and covered with a damp cloth. At room temperature, they should germinate in 3-4 days. If you need to raise the temperature, then cover the saucer with polyethylene.

Seedling Care
Seedling care consists of ensuring the correct climatic conditions, regular irrigation, feeding, hardening.
As soon as the shoots appear, the temperature must be reduced to +7 ... + 10 ° С - at higher rates, the plants begin to stretch. Be sure to organize high-quality lighting of seedlings: if this is not done, it begins to stretch toward the light source, for example, a window. To exclude this, the boxes with plants are illuminated with fluorescent or LED lamps.
When 2-3 real leaves appear in seedlings, they must be dived - this is a process in which plants are transplanted into individual cups and shortened the central root. Thanks to this procedure, not only one root root is formed, but also the side roots begin to develop, which improves the nutrition and development of the plant as a whole.

Water the cabbage from the watering can after the soil is slightly dry. Waterlogging crops should not be. In phase 2 of the leaves, the plants are fed with a balanced fertilizer, in which equal proportions of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium are present. The second top dressing is carried out 2 weeks after the first, immediately before planting seedlings in the ground.
Video: The secrets of growing cabbage seedlings
Harden plants begin 1 week before planting. It is carried out for 1 hour on the first day, gradually increasing the time spent in the air. Hardening reduces the degree of stress for plants from temperature extremes indoors and outdoors.

A week before planting, watering is stopped in order to stop the growth of plants. On the eve of planting, abundant watering is carried out - this will help to extract the plants from the pots. If they grew in paper or peat containers, then they are planted in the ground without removing seedlings.
Open transplant
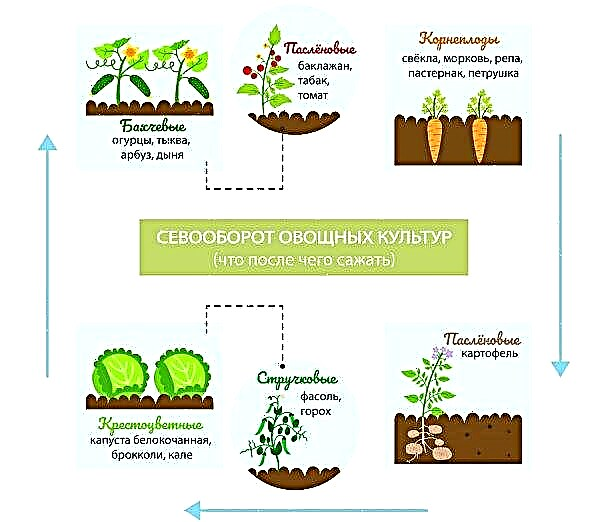
First of all, you need to consider that seedlings can not be planted on the site where cruciferous or other leafy vegetables grew in the previous season. During growth, enough pathogens and pests accumulate in the soil to reduce the yield of planted plants. You can return to such a site after 4 years.
Important! White cabbage needs a lot of light, so the beds should not be obscured by trees or buildings. Without good lighting, plants will not head out.
Cabbage is demanding on the quality of the soil. Evaluate the quality of the site visually, according to the condition of the plants growing nearby: if they look healthy, then the soil is fertile enough and you can add only half the dose of fertilizer. The depleted area must be fertilized.

Ankoma leaf rosette may be horizontal or only slightly raised. She needs about 50 cm of free space. Planting is carried out in rows, placing plants at a distance of 0.5 m from each other, and rows - at a distance of 0.6–0.8 m. Cabbage can be planted and compacted - provided that some of the heads will be harvested for use until the time of the main harvest the crop. When planting in the landing trenches, humus or rotted manure is introduced at the rate of 5-8 kg / m².

Landing dates - from late May to early June. The age of the plants at this point will be 35–40 days. Planting depth should be the same at which the plants grew in containers. Planting plants in the ground is necessary in warm, dry weather and in the absence of soil frost in the morning.
Follow-up care
Directly when planting, plants are abundantly watered, the soil around the roots is compacted. Further care will consist of watering, fertilizing, hilling, tillage and pest control.
Watering and fertilizer
White cabbage is extremely demanding on moisture. In normal weather, it is watered once a week. The water consumption rate is 3-5 liters for one plant, its temperature is + 18 ° С. Watering with cold water is dangerous, as it provokes the development of fungal diseases - blackleg, rot. If it rains, then additionally watering the plants is not necessary.

It will be great if you can use drip irrigation. With such irrigation, water is supplied to the root zone with a dropper-dropper: the soil is moistened with high quality and immediately next to the roots of the plant, and much less water is used.
Important! Be sure to water the plant evenly - otherwise the head of cabbage may crack. The same thing happens with heavy watering at the moment when the cabbage has finished ripening.
The first feeding of cabbage is carried out 2 weeks after planting. For one plant, a solution of 0.5 l of rotted manure is used: it is prepared from 1 part of the substance and 10 parts of water. If chicken droppings are used, the amount of water in the solution is increased by 2 times. After top dressing, the soil is sprinkled with ash - this is an additional source of potassium, as well as a means of combating some pests (the norm is 1 glass / m²).
The second top dressing is carried out 2 weeks after the first. Frequency is maintained until the end of July. In July, it is recommended to feed with an increased dose of potash fertilizers.

Pest and Disease Control
Healthy plants are less susceptible to attack by pests and diseases and better resist them. The danger of pests lies in the fact that they spoil the plant tissue, and also are carriers of viral diseases. Through holes made by insects, pathogens enter the plant, which can lead to their death.
The plan of preventive measures necessarily includes weed control, removal of organic residues after harvesting, digging a plot in the fall, and crop rotation.
The main pests of cabbage:
- Cabbage Moth - These are 1.5 cm long moths that damage leaves. Their larvae are green caterpillars that match the leaves in shade. For processing from them, systemic insecticides are used, for example, Ditox, biological ones - Fitoverm, chemical ones - Borey, Decis Expert, Antitlin.

- Cabbage Covert Hunter - black beetle with a long and thin rostrum. Its larvae gnaw passages, moving to the root system of the plant, which causes its death. During the growing season, Alpha-Amiprid is used for spraying.

- Fleas - a family of beetles up to 2.5 mm in size, of different colors. They feed on the flesh of the leaf. For spraying, Borey, Ditox, Di-68, and Antitlin are used.
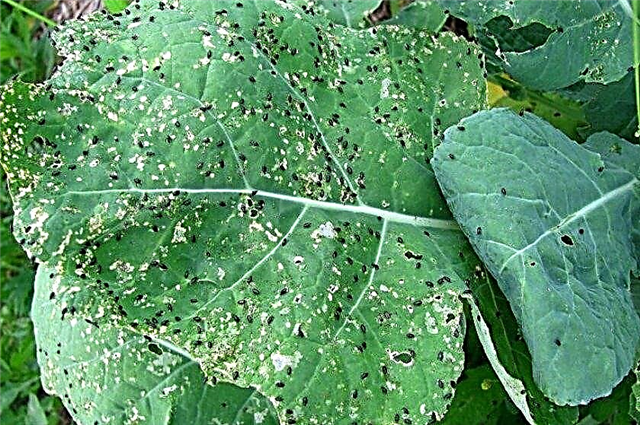

- Cabbage white - Mealy-white butterfly with a dark edging of wings. Her caterpillars damage the leaves. For treatment, Barguzin, Borey, Fufanon are used. Some gardeners practice netting. As a result, butterflies and moths cannot land on plants and lay eggs.

- Slug - the inhabitants of most gardens. They not only damage the cabbage, but also leave sticky mucus along the route. To combat them, the aisles are sprinkled with crushed shell rock or sawdust - the texture of the material is too hard for the slugs, and they do not overcome such a barrier. Also, crops are sprayed with a 0.5% solution of copper sulfate.

- Aphid often affects vegetable crops. These are small green insects that feed on plant sap. They settle on the underside of the leaf outlet. Are carriers of viruses. And the sticky "honey syrup" secreted by aphids becomes a breeding ground for the development of sooty fungi. To combat aphids, spray with a solution of garlic or tobacco.

Prevention of fungal diseases consists in spraying crops with solutions based on copper - it can be a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid or 0.5% copper sulfate. Copper ions are activated in the morning, interacting with dew. The result is an invisible leaf coating that neutralizes pathogens. It is recommended that plants be treated before signs of disease appear, as well as after rains.
Did you know? Cabbage helps with the slow healing of external wounds. Fresh leaf compresses are especially effective for damage to the lower leg.
The main diseases:
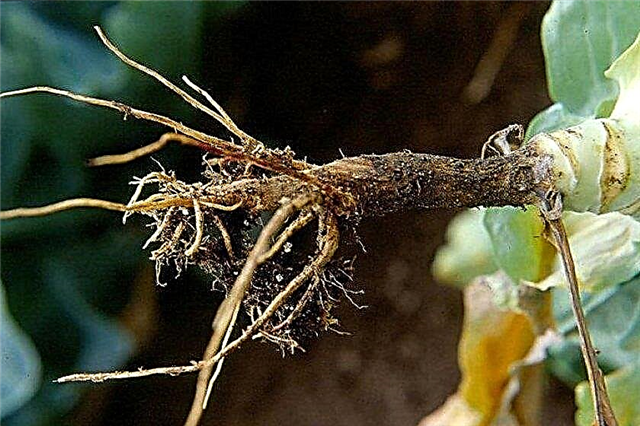
- Blackleg - This is a fungus that develops with high humidity. It affects the root neck - it blackens and rots. Sick plants are burned, and the beds are treated with a solution of potassium permanganate 3%.

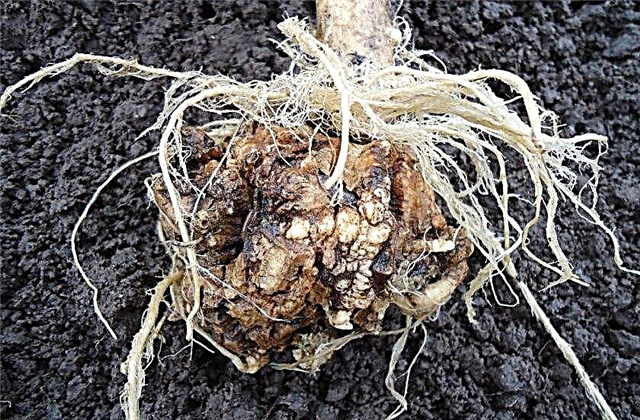
- Kila - A dangerous disease that affects plants in acidic soil. Thickened growths form on the roots. These are not the roots. They cannot consume nutrients from the soil. The roots themselves die while causing the death of cabbage. Affected plants are removed from the site along with the soil, and the area where they grew is sprinkled with plenty of lime. The disease is not treated, and it is possible to return with cabbage to such a site no earlier than in 5-7 years.

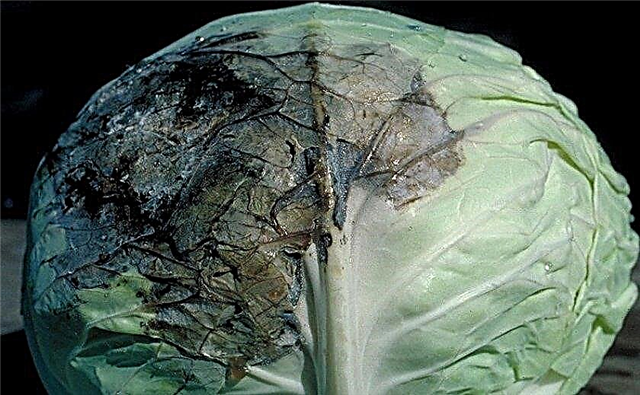
- Mucosal bacteriosis - These are the blackened wet parts of the leaves that start to smell unpleasant. Subsequently, the head of cabbage is completely amazed.Such plants are removed, and the beds are treated with Trichodermin.
- Peronosporosis (downy mildew) - manifested by yellowish spots on the leaves. They gradually increase, which leads to the death of the sheet. It is recommended to remove infected parts of plants, and treat crops with Oxychom.

Harvesting and storage
Technical maturity of the variety occurs 120 days after emergence. But you can eat cabbage earlier. Mid-late varieties are good in that the collected heads of cabbage can be stored for up to 6 months without loss of quality.
Did you know? Cabbage is often applied to the face to clear acne-prone skin. It has been proven that it has many antioxidants that protect the epidermis from damage, especially from ultraviolet radiation.
Cabbage will be well stored on trellised shelves in a cool, dry and dark pantry for long months. Lattice shelves allow the flow of air to blow around the heads of cabbage, preventing the formation of mold. They can also be stored in nets. Before storage, remove excess outer leaves; slugs may be under them!

Ankoma variety is unpretentious: it can be grown on any soil, as well as under a variety of climatic conditions. Observing the basic rules for caring for plants, you will provide yourself with a good harvest of these healthy vegetables.