Tomato cultivation is often complicated by infection of the crop with late blight, which negatively affects the quality and quantity of the crop. In today's article, the causes of the disease, methods of control and prevention are considered.
Reasons and conditions of occurrence
Late blight is a rather dangerous disease that can pass from one plant to another. Spores of pathogenic fungi that live in the soil provoke the disease and remain on garden tools, if their disinfection is neglected.

Reasons that contribute to the appearance and propagation of fungal infection:
- close proximity to other nightshade crops;
- plant residues in the area selected for planting;
- excessive watering and excess fertilizer, especially organic;
- increased air humidity (dense landings, lack of ventilation);
- lack of trace elements in the soil;
- wrong way of watering (foliage irrigation);
- sudden changes in temperature.
Blight gradually destroys the bushes:
- first affects the lower leaves;
- then the stems and flower buds;
- inflorescences and fruit ovaries;
- subsequently, the fruits are affected, the entire bush dies.
In just a few days, the fungus is able to destroy the entire planting.
Did you know? 70 species of fungi are known that live on all continents of the Earth, even in Antarctica.
Signs of late blight on tomatoes
In order not to miss the beginning of the epidemic, you need to carefully examine the tomato bushes at each stage of their development.
Symptoms of late blight:
- a white coating appears on the leaves, which eventually turns into brown spots. Foliage turns yellow, dries and flies;
- brown, irregularly shaped spots cover the shoots of the plant;
- inflorescences change color: turn yellow or darken, dry out and fly around;
- black dots form on the fruits, which quickly increase. The skin softens and the flesh begins to rot, spreading an unpleasant odor.

How to deal with late blight on tomatoes in a greenhouse folk remedies
It is not always possible to process the culture with chemical means, for example, at the stage of formation of fruit ovaries, this is prohibited. Folk remedies come to the rescue.
Saline solution
Salt solution drags the plants with a kind of film that interferes with the penetration of new spores, slowing down the development of an existing fungus. To prepare the solution for each liter of water add 100 g of salt, the amount depending on the size of the lesion. Stir the mixture until the crystals are completely dissolved. Only affected plants should be sprayed. In open ground, the procedure is repeated after precipitation.
Soda
Soda, in addition to the destruction of fungi, will also serve as additional fertilizing. For the preparation of funds take 3-5 tbsp. l soda and 2 tbsp. grated laundry soap in 8-10 liters of water. Thoroughly mixing the mixture, apply to the culture by spraying in the morning or evening. In open ground, the procedure is carried out in the evening when there is no dew. After rain, the treatment is repeated. Spraying with soda can be repeated once every 2 weeks, if necessary.
Important! The first procedure of any treatment is carried out no earlier than 2 weeks after planting.
Ash
Wood ash is often used by gardeners as fertilizer and the prevention of insects. It copes well with late blight.
The solution must be properly prepared:
- 5 kg of ash are mixed in a 10 liter bucket.
- For 3 days, stirring, insist.
- The mixture is brought to a volume of 30 l by adding water.
- A liquid or grated soap is added to the finished solution to improve adhesion.

And in the greenhouse, and in open areas, they are sprayed three times per season:
- during the period of active growth;
- during the formation of inflorescences;
- during the formation of fruit ovaries.
Kefir
Sour milk bacteria contained in kefir are able to suppress pathogenic microorganisms. The product is safe for tomatoes, which allows for multiple processing. Diluted kefir with water in a ratio of 1: 5. It is advisable to ventilate the greenhouse after spraying well. In open ground, repeat after rain.

Copper wire protection
One of the effective methods is the use of copper wire. A stem punctured by a piece of wire receives microdoses of copper, which normalize all metabolic processes in the tissues.
Our gardeners apply the method differently:
- The wire is carefully cleaned with an emery and calcined.
- Cut lengths of 2-3 cm (thickness of the stem).
- The shoot is pierced at a height of 10-12 cm from the surface of the earth.
- The ends of the wire are neatly bent.
The procedure is the same for the greenhouse, and for open beds. It should be borne in mind that the stems should be strong enough.
Did you know? They discovered and patented a method of protection. plants copper wire German scientists. They were prompted by this observation: near the smelters there was not a single case of infection with late blight.
Greenhouse Prevention
An ideal environment for the development of fungal diseases is high humidity, the risks in the greenhouse increase. Therefore, the main measure is compliance with the humidity regime, the frequency of watering.
In addition, they take such preventive actions:
- Regularly ventilate the room.
- Low-growing varieties are chosen for planting.
- High bushes must be tied so that the fruits do not fall on the ground.
- Do not neglect pinching, removing the lower leaves and thinning out the planting.
- Maintain the distance between plants, since a dense planting creates increased humidity.
- Do not water after 17 hours, the moisture does not have time to evaporate until night.
- Solanaceous crops are not planted close to the greenhouse: potatoes, eggplant.
- After each manipulation, garden equipment is disinfected.
Useful Tips
Experienced gardeners have their secrets for preserving a tomato crop.
Useful recommendations:
- Prevention begins with the disinfection of planting material and soil.
- Normal iodine will help strengthen the immunity of a tomato. Open vials with an antiseptic are suspended in a greenhouse above the bushes.
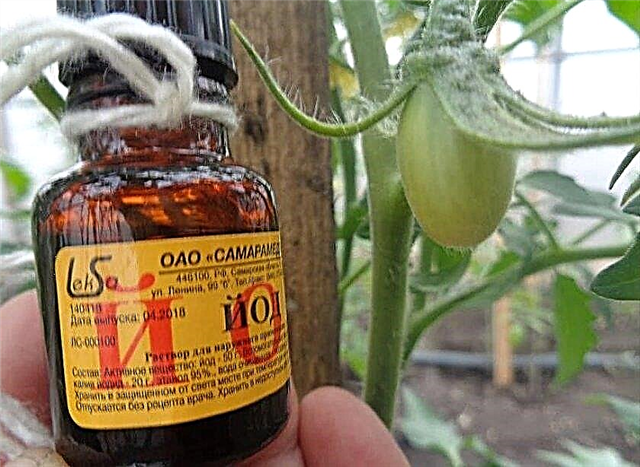

- Spraying with boric acid is an excellent prevention of diseases and pests. In addition, the element is necessary to improve the size of the fruit and taste.
- In a greenhouse, it is best to use the drip-subsoil irrigation method. Moisture goes directly to the roots, the amount of fluid is easy to regulate.
- The use of mulch will reduce watering, retain moisture in the soil, preventing overmoistening of the air.
- Be sure to disinfect the entire room after harvesting: walls, doors, windows.
Disease resistant varieties
From year to year, breeders from many countries are introducing new varieties of tomatoes resistant to fungal diseases.
The most popular varieties:
a) for the greenhouse:
- Academician of Sugars;
- "Budenovka";
- "Resonance";
- "Snowdrop";
- "Union 8 f1";

b) for open ground:
- Anyuta;
- "Minion of fate";
- Betta
- Cardinal
- "Pepper-shaped striped."
Important! After harvesting, the soil is thoroughly cleaned of plant debris, if necessary, replace the top layer.
For the health of your landings, it is important to take preventative measures, observe the conditions for caring for the crop. Note also that the resistance of the variety from late blight does not guarantee its absence if errors are made in agricultural technology.